Home » Active Directory Management Tools: Must-Have Features » Strengthening Access Controls through Active Directory Auditing
Strengthening Access Controls through Active Directory Auditing
Learn about the key concepts of Active Directory auditing, including strategic policy configuration, meticulous log management, and automated monitoring.
Explore the chapters:
- Chapter
- Active Directory Management Tools
- Active Directory Group Policy Management
- Active Directory Security
- Active Directory Management
- Active Directory Disaster Recovery
- Active Directory Auditing
- Active Directory Groups
- Disable Active Directory
- Active Directory Reporting
- Active Directory Backup
- Active Directory Forests
- Active Directory Monitoring
- Chapter
- Active Directory Management Tools
- Active Directory Group Policy Management
- Active Directory Security
- Active Directory Management
- Active Directory Disaster Recovery
- Active Directory Auditing
- Active Directory Groups
- Disable Active Directory
- Active Directory Reporting
- Active Directory Backup
- Active Directory Forests
- Active Directory Monitoring
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Digital assets form the bedrock of organizational value, which means that securing the integrity of these resources is more critical than ever. Active Directory (AD) stands at the center of a secure infrastructure, providing identity management and access controls that govern user interactions with network resources.
This article delves into essential AD strategies for strategic audit policy configuration, meticulous log management, and the implementation of regular reviews and advanced automated monitoring. We aim to provide administrators and IT professionals with actionable insights to enhance the auditing capabilities of their AD environments while safeguarding their organizations’ digital environments.
Summary of Key Concepts Related to Active Directory Auditing
| Best Practice | Description |
| Understanding Active Directory auditing | Active Directory (AD) auditing enhances security, compliance, and operational integrity by tracking changes such as user logins and policy modifications. The various audit types include security auditing for tracking potential breaches, Directory Service Access for monitoring AD object interactions, account management for observing user/group lifecycle changes, and policy change auditing for recording group policy alterations. These audits enable organizations to detect unauthorized activities, conduct post-breach analysis, and uphold a secured, compliant IT environment. |
| Challenges in Active Directory auditing | The auditing processes can impact system performance and scalability, as the multitude of logged events can slow down domain controllers. This creates a need for balancing oversight and maintenance with the help of specialized tools and strategic auditing. Compliance and forensic readiness demand strict policy adherence and log retention to align with standards like GDPR and HIPAA, requiring comprehensive logs for regulatory fulfillment and detailed tracing for security investigations. |
| Best practices for Active Directory auditing | Strategic audit policies in AD auditing are essential, focusing on selecting policies that meet security, compliance, and operational needs without overwhelming systems. Effective log management involves using strict access controls and ensuring that logs are unalterable and centrally stored in order to maintain their integrity for compliance, trend analysis, and incident response purposes. Combining regular audits and automated monitoring fortifies AD environments against security breaches by continually checking user rights and configurations and quickly reacting to suspicious activities with real-time alerts, thereby striking a balance between manual oversight and automated processes. |
| Cayosoft and Active Directory auditing | Cayosoft Guardian is a solution for securing and maintaining compliance in AD and hybrid AD environments by offering real-time monitoring, automated recovery, and detailed reporting to protect against threats and aid in management decisions. It supports strategic audit policies by automatically tracking crucial system changes and security adjustments, enabling targeted policy creation and efficient oversight while safeguarding log management by consolidating log data and providing advanced security to ensure data integrity. |
| Implementing Cayosoft for Effective Auditing | In a simulated scenario, a company called NexTech Solutions is undergoing a major reorganization and decides to utilize Cayosoft Guardian to conduct an internal audit of its AD setup to ensure that all modifications align with security policies and compliance standards. Cayosoft Guardian aids in real-time monitoring and auditing of new user accounts, group memberships, and access rights changes, providing change history logs for audit team review, discrepancy identification, and instant rollback of unauthorized changes. |
Understanding Active Directory Auditing
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft-developed directory service integral to Windows Server ecosystems that centralizes the management of users, computers, and other security entities across a network. It organizes data hierarchically, enabling efficient user management, policy application, and access control. Known for its scalability, AD supports key features like the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), single sign-on (SSO), and a structured domain environment. It facilitates robust resource management as well as security for any organization size or type. For more information on Active Directory, please see Microsoft’s overview.
The Purpose of AD Auditing
AD auditing is intended to ensure the security, compliance, and operational integrity of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Tracking and logging changes made within AD—such as new user logins, policy modifications, and permission adjustments—gives administrators critical insights into network activity and user behavior. This helps them quickly identify and mitigate potential security threats and ensures adherence to regulatory standards and internal policies. Effective AD auditing can reveal patterns consistent with unauthorized or malicious activities, support analysis in the event of a breach, and enable organizations to maintain a continuously secured and compliant environment.
Types of Audits
There are several types of audits that cater to a variety of security and operational requirements:
- Security auditing tracks logins, account lockouts, and other security-related events, offering visibility into potential breaches.
- Directory Service Access auditing provides insights into who accessed or modified AD objects and attributes, which is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information.
- Account management auditing checks user and group lifecycle events, such as creating, deleting, or changing accounts or groups.
- Policy change auditing records alterations in group policies, which helps ensure intended policy adjustments and adherence to best practices.
These audit types collectively form a comprehensive monitoring system to aid in maintaining the health, security, and compliance of IT environments managed by Active Directory.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, Office 365

Unified Console
Use a single tool to administer and secure AD, Azure AD, and Office 365

Track Threats
Monitor AD for unwanted changes – detect for security or critical functions

Instant Recovery
Recover global enterprise-wide Active Directory forests in minutes, not days
Challenges in Active Directory Auditing
Volume and Complexity
Navigating the volume and complexity of data generated by AD auditing can be daunting. Organizations face the challenge of sifting through a sea of detailed logs that record every login attempt, access request, and directory change across an expansive network of users and machines.
The difficulty lies not only in the quantity of data but also in its variety and the knowledge required to interpret it accurately. Events that seem inconspicuous at first glance may hold the key to identifying potential security threats, policy violations, or system misconfigurations. Analysts need advanced tools and expertise to filter, correlate, and analyze this information to discern actionable insights without being overwhelmed by the sheer scale of the audit trail.
Performance and Scalability
The introduction of meticulous auditing policies can lead to a substantial increase in the number of events that domain controllers must process and log, which, in turn, can degrade overall system performance. Every tracked operation consumes computational resources, causing a potential slowdown in user authentication processes and resource access. This performance hit is compounded as organizations scale up, adding more users, devices, and applications to their networks.
IT administrators must strike a fine balance between achieving comprehensive oversight through AD auditing and maintaining the swift, responsive performance that users expect. This requires a strategic approach to selecting only essential auditing activities and possibly leveraging additional resources or specialized software to handle the increased workload without impacting the user experience.
Compliance and Forensic Preparedness
Ensuring compliance and forensic readiness within the sphere of AD auditing is a crucial concern for businesses operating in heavily regulated industries. The complexity of aligning AD audit practices with varied compliance standards—such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and more—requires a strict approach to policy configuration and log retention.
Audit logs must be both comprehensive and retrievable to satisfy regulatory requirements for tracking access to sensitive data and to demonstrate that adequate security controls are in place.
In the context of forensic analysis, the ability to trace an entire sequence of events to its origin is imperative for investigating security breaches or insider threats. Achieving this level of detail requires the preservation of logs over extended periods, the organization of data to ensure its integrity, and the implementation of protection measures to prevent tampering.
Best Practices for Active Directory Auditing
Implement Strategic Audit Policies
Strategic audit policies are crucial for AD auditing. Putting them in place involves the careful selection and implementation of audit policies that are aligned with an organization’s specific security objectives, compliance requirements, and operational performance standards. This tailored approach ensures that only relevant activities are logged—such as user authentication, privilege escalations, and policy changes—thereby avoiding data bloat and minimizing the impact on system resources.
Configuring audit policies with precision helps create a concise trail of critical events without generating an overwhelming volume of logs, which could obscure meaningful insights. By reviewing and updating these policies in response to evolving IT landscapes and emerging threats, organizations can maintain a resilient and responsive auditing system that not only protects against potential breaches but also supports a strong compliance and forensic posture.
Focus on Log Management and Security
Log management and security ensure that the information contained within audit logs is neither compromised nor mishandled. Effective log management starts with stringent access controls, permitting only authorized personnel to view or handle the logs, thereby safeguarding them against unauthorized disclosures or alterations. Log security is further reinforced by making them immutable, preventing any tampering that could undermine their reliability as a source of truth in forensic investigations.
Centralized storage of these logs is very important, offering a secure and consolidated repository that simplifies management and analysis. Consistent and secure log retention practices are essential not just for meeting compliance obligations but also for providing historical data for trend analysis and long-term incident response. Investing in robust log management and security protocols is thus critical for organizations to maintain the integrity of their AD auditing processes and uphold their overall security frameworks.
Conduct Regular Reviews and Set Up Automated Monitoring
Regular reviews and automated monitoring are vital practices in sustaining a secure and compliant AD environment. Conducting periodic audits enables organizations to evaluate user access rights and AD configurations, ensuring that only appropriate permissions are granted and aligned with current job requirements. This proactive review helps promptly identify and resolve any irregularities or excess privileges that could lead to security breaches.
In parallel, deploying automated monitoring systems is key to maintaining ongoing vigilance. These systems can provide real-time alerts upon detecting unusual activity, such as anomalous login patterns or unauthorized access attempts, facilitating immediate response to potential security incidents. By intertwining regular manual reviews with the efficiency of automated tools, organizations can create a comprehensive oversight mechanism that effectively guards against internal and external threats while also keeping pace with the dynamic nature of user roles and access needs within the AD infrastructure.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams
| Platform | Admin Features | Single Console for Hybrid (On-prem AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams) | Change Monitoring & Auditing | User Governance (Roles, Rules, Automation) | Forest Recovery in Minutes |
| Microsoft AD Native Tools | ✓ | ||||
| Microsoft AD + Cayosoft | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Cayosoft and Active Directory Auditing
Cayosoft Guardian is designed to be a comprehensive solution for ensuring the security and compliance of AD and hybrid AD environments. Its primary purpose is to safeguard critical IT infrastructure from both internal and external threats by providing real-time monitoring, automated recovery, and in-depth reporting.
Cayosoft Guardian helps organizations minimize the risks associated with AD changes and deletions. The software delivers peace of mind to IT administrators and security professionals by automating the detection, alerting, and quick recovery from undesired or malicious changes in Active Directory and Office 365, maintaining the integrity and reliability of IT operations. The software’s robust audit trails and intuitive monitoring tools facilitate strategic decision-making and compliance with regulatory requirements, making Guardian an essential asset for modern, security-conscious enterprises managing complex IT environments. Guardian also has threat analysis to scan and actively monitor for AD and Azure Entra ID threats. The out-of-the-box configuration requires no additional configuration to enable monitoring and alerts.
The following are areas where Cayosoft Guardian can help administrators implement the best practices associated with auditing AD.
Strategic Audit Policies
Cayosoft Guardian facilitates strategic audit policies by providing administrators the tools they need to enforce comprehensive audit strategies. With Cayosoft Guardian, critical system changes, privileged operations, and security adjustments within the Active Directory ecosystem are tracked automatically. This targeted approach to policy configuration reduces overhead and captures only the most pertinent data, providing focused oversight into the operational integrity of the AD environment.
Log Management and Security
Effective log management is a cornerstone of robust Active Directory auditing. Cayosoft Guardian creates events based on activity within AD and Azure Entra ID offering clear and actionable insights. This allows security teams to respond swiftly to potential threats and streamline the identification of anomalous patterns, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of the organization.
Regular Reviews and Automated Monitoring
A proactive review process is integral to maintaining the health and security of any Active Directory infrastructure. Cayosoft Guardian contributes to this by providing both scheduled auditing and continuous, automated monitoring. It systematically reviews configurations and access patterns, sending regular reports to administrators, which facilitates the enforcement of governance policies.
Cayosoft Guardian’s automated monitors constantly review the Active Directory environment for unexpected changes or actions, offering real-time alerts to possible security incidents. With these capabilities, Cayosoft Guardian helps organizations identify and rectify issues swiftly, minimizes risk exposure, and ensures continuous compliance with internal and external standards.
Implementing Cayosoft for Effective Auditing
Audit Objective
This audit’s intent is to verify that only authorized changes have occurred within the Active Directory implementation. The goal is to ensure that user permissions and roles reflect the new organizational structure, no unauthorized access has been granted as part of the changes, and any anomalies or policy violations are identified and resolved.
Watch a demo video of Cayosoft’s hybrid user provisioning
Pre-Audit Setup
Administrators and engineers at NexTech Solutions have decided to implement Cayosoft Guardian to assist with the audit process. NexTech Solutions configures Cayosoft Guardian to track specific AD objects and attributes relevant to their reorganization. They will use Guardian to customize role assignment changes, group membership updates, and permission modifications.
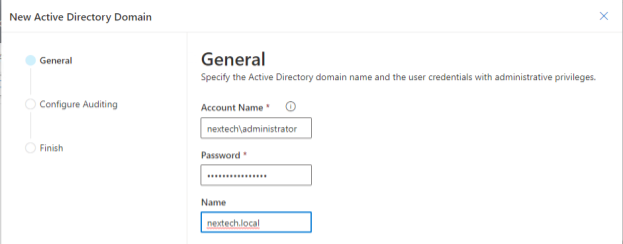
Administrators start by installing Cayosoft Guardian. After the installation is complete, admins will connect the domain to Caysoft Guardian, as shown below.
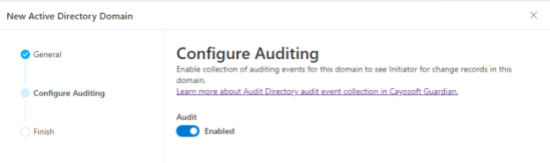
As part of the wizard for adding the domain, there is also an option to enable auditing. NexTech’s administrators will use the built-in auditing function of Guardian to assist with the audit.
Real-Time Monitoring
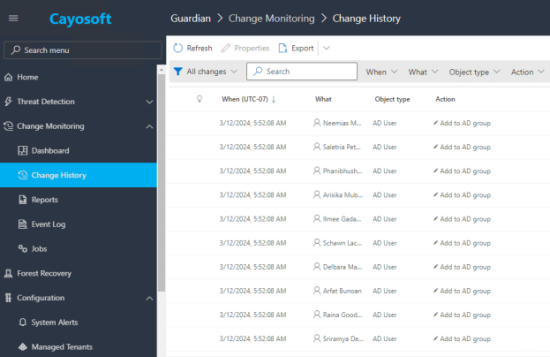
With the domain connected and auditing enabled, Cayosoft Guardian’s real-time monitoring detects all the Active Directory changes made during the restructuring period. This includes new user account creations, changes in group memberships, and modifications of access rights.
For example, as part of the restructuring, new security groups have been created for each department. One of the administrators has executed a Powershell script that will add all of the users in the IT department to the group “IT.” From the image below, it can be seen that Cayosoft Guardian has tracked all of the changes made for those users.
Review and Analysis
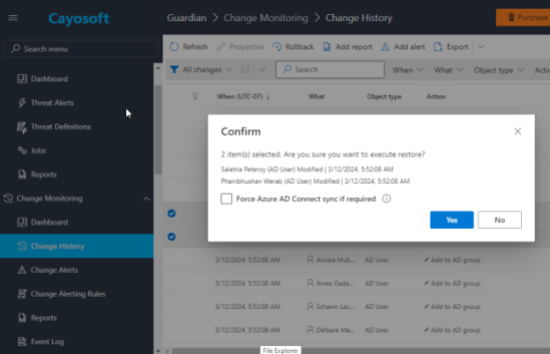
The audit team reviews the change history provided by Guardian, comparing the logged changes against the approved restructuring plan. They find a few discrepancies where permissions were incorrectly assigned to a few accounts. Guardian offers a single-click rollback option that allows administrators to highlight the discrepancies and reverse the actions taken instantly.
In this case, there were two users who had switched departments, but the department property in AD had not been updated. Using the rollback feature, admins were able to undo the changes and correct the properties for these users.
Post-Audit Documentation
Finally, the audit team creates a full audit trail leveraging Cayosoft Guardian’s data exports to ensure that there’s documentation to support their findings and actions, which serves as proof of compliance and due diligence for the company.
Learn why U.S. State’s Department of Information Technology (DOIT) chose Cayosoft
Last Thoughts
Auditing Active Directory is not just a one-time endeavor: It’s a continual process of vigilance and refinement. Combining regular manual reviews with the precision of automated monitoring provides a robust defense against potential issues in security. Through diligent log management and adherence to best practices, organizations can ensure that their AD systems remain secure, resilient, and aligned with evolving security landscapes. By prioritizing these efforts, IT professionals can effectively protect their organizations from the myriad of threats that target valuable digital assets
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content