Home » Your Guide to Secure Endpoint Management: Essential Microsoft Intune Features » Choosing Your License: A Practical Guide to Microsoft Intune Licensing
Choosing Your License: A Practical Guide to Microsoft Intune Licensing
Learn about the various Intune licensing options, plans, and add-ons, their features, costs, and ideal usage scenarios to optimize cost and security coverage.
Explore the chapters:
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based unified endpoint management (UEM) solution that enables organizations to manage and secure devices, applications, and data across multiple platforms. Fundamentally, it allows IT administrators to enroll, configure, and update devices, apply security policies, deploy and manage applications, protect data, and monitor device status.
Choosing the wrong Microsoft Intune license can cost you more than money—it can compromise security coverage, limit management capabilities, and create operational blind spots that attackers exploit. With hybrid work now permanent and device ecosystems more complex than ever before, your Intune licensing strategy determines whether you’re managing endpoints or merely monitoring them.
This article discusses various Intune licensing options, plans and add-ons. We also discuss their essential features, how they can be acquired (standalone or bundled), and their associated costs.
Summary of Intune licensing plan concepts
This table summarizes the licensing concepts that IT admins should know when dealing with Intune licensing.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Intune Plan 1 | A cloud-based endpoint management solution that helps organizations securely manage devices, apps, and data across multiple platforms |
| Microsoft Intune Plan 2 | Extends Plan 1 with advanced endpoint security, enhanced compliance policies, and granular access controls for improved device and data protection |
| Microsoft Intune Suite | Provides access to critical advanced endpoint management and security features in Intune |
| Device-based licensing | Lets devices be directly assigned with this license |
| License requirement analysis | Comparing the license features with the actual requirements and then deciding on the license type to purchase |
| License management and cost optimization | Monitoring licenses and usage across the tenant to increase cost-effectiveness |
Learn About The First-Ever Monitoring and Rollback for Microsoft Intune
Intune license overview
Microsoft organizes its Intune licenses into several tiers, each designed to meet various organizational needs and complexity levels. Understanding the distinctions between these licenses will help admins align licensing decisions with security and budget requirements.
| License | Price per user per month with annual commitment | Key Features | Ideal Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intune Plan 1 (per-user) | ~$8.00 |
| Small to mid-sized organizations needing standard device/app management |
| Intune Plan 2 (per-user add-on) | ~$4.00 |
| Organizations looking to extend Intune Plan 1’s capabilities with specialized device management or enhanced secure access for mobile apps Note: Plan 2 is an add-on to Plan 1 (requires Plan 1 base license). |
| Intune Suite (per-user bundle) | ~$10.00 |
| Large organizations or those with high security/compliance needs |
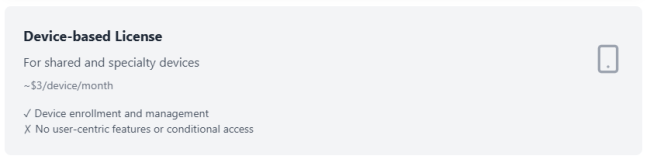
| Device-based license (“Intune Plan 1 Device”) | ~$3.00 |
| Shared devices, IoT, or situations where devices are not tied to individual user accounts. |
It is important to note that all the prices indicated are US commercial rates with annual commitment and are subject to change.
Microsoft Intune Plan 1
Microsoft Intune Plan 1 is the foundation for most enterprise endpoint management implementations, offering a comprehensive suite of device and application management capabilities across all major platforms. This license tier addresses core UEM requirements, including device enrollment, application management, and basic security controls.
Plan 1’s robust capabilities support organizations moving from traditional on-prem management solutions to cloud-based architecture, providing a solid foundation for their endpoint management needs. These capabilities include the following features:
- Cross-platform endpoint management: Plan 1 provides extensive support for managing various endpoint devices and operating systems from a single console, including laptops, desktops, virtual machines, Windows, macOS, Linux, and Android devices.
- Built-in endpoint security: Plan 1 includes fundamental endpoint security features through integration with Microsoft Defender and Windows Security, leveraging Intune’s security baselines and automated vulnerability assessments to reduce risk.
- Mobile Application Management (MAM): This feature allows for the management of applications, particularly on mobile devices, without necessarily requiring the device to be enrolled and fully managed by Intune. MAM is particularly useful for supporting bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios, where IT needs to secure corporate data within applications without interfering with the user’s data or requiring full control over their device.
- Endpoint analytics: Plan 1 includes basic endpoint analytics capabilities, which provide IT admins with insights into device performance and health. These analytics often provide health scores and data-driven recommendations to improve productivity and the user experience.
- Microsoft Configuration Manager: Although Microsoft Configuration Manager (formerly System Center Configuration Manager) is primarily an on-premises management solution, Plan 1 grants the rights to use it in co-management scenarios, allowing administrators to potentially co-manage devices using both Intune and Configuration Manager.
Many Microsoft bundles include Intune Plan 1’s feature set by default. For example, all Microsoft 365 E3/E5, Enterprise Mobility + Security E3/E5, Business Premium, and F1/F3 education plans ship with Intune Plan 1 rights. So, a medium-sized company with any of these subscriptions doesn’t need to buy Intune separately.
Watch a 15-minute Demo of Microsoft Intune Change Monitoring and Recovery
Microsoft Intune Plan 2
While Microsoft Intune Plan 1 provides the foundational capabilities for modern endpoint management, some organizations require more specialized tools. Microsoft Intune Plan 2 is not a standalone product for new customers but an add-on to Intune Plan 1. This means that an organization can enhance its Plan 1 license with the features included in Plan 2, catering to its specific, often more complex, enterprise needs. This licensing option is also part of the broader Microsoft Intune Suite.
Plan 2 introduces functionalities such as the following:
- Microsoft Tunnel for Mobile Application Management (MAM): This feature provides a lightweight VPN gateway solution that allows applications on unenrolled iOS and Android devices (managed via MAM policies) to access on-premises resources securely. Microsoft Tunnel is particularly useful for BYOD scenarios where full device enrollment is not desired or feasible, but secure access to internal applications and data is still required.
- Management of specialty devices: While Intune Plan 1 offers basic support for specialty and shared devices, Plan 2 provides more comprehensive device management and protection features tailored for specialized devices, including conference room meeting equipment and large smart-screen devices.
- Firmware-over-the-air (FOTA) updates: Intune Plan 2 enables remote FOTA updates for supported Android Enterprise devices from specific OEMs (such as Zebra and Samsung). This allows administrators to manage and deploy firmware updates wirelessly, which is critically important for maintaining the security and functionality of these devices—especially those used in business-critical operations.
Organizations with significant mobile workforces requiring secure access to internal resources benefit substantially from Plan 2 capabilities. Field service organizations, healthcare providers, and financial services firms often require the enhanced mobile security that Microsoft Tunnel provides. The per-application VPN capabilities enable secure data access while respecting privacy boundaries and regulatory requirements.
Learn the best practices for Intune monitoring, security, and recovery
Microsoft Intune Suite
Intune Suite is the highest tier, packaging all advanced Intune capabilities into one subscription. It includes everything in Plan 1 and Plan 2, plus additional premium add-on features, all integrated into its subscription price.
The Intune Suite bundles several powerful tools, each addressing specific advanced IT needs:
- Microsoft Intune Remote Help: This feature enables helpdesk personnel to establish secure connections to managed devices to provide remote assistance and troubleshoot issues. It is invaluable for supporting remote workers or users in different locations, allowing support staff to diagnose and resolve problems efficiently without physical access to the device.
- Microsoft Intune Endpoint Privilege Management: Maintaining security through the principle of least privilege can be difficult to reconcile with the need for user productivity, particularly when tasks demand higher-level permissions. Endpoint Privilege Management allows standard users to perform specific tasks or run applications that require elevated privileges, as approved by organizational policy, without granting them full local administrator rights, which significantly reduces the attack surface associated with widespread admin rights.
- Microsoft Intune Advanced Analytics: Proactive management requires a deep understanding of endpoint health, performance, and user experience. The advanced analytics feature provides IT administrators with data-driven insights and metrics on their endpoint devices, which empowers them to proactively understand, anticipate, and, ultimately, enhance the end-user experience.
- Microsoft Intune Enterprise Application Management (EAM): This tool simplifies the lifecycle management of Win32 applications by providing a securely hosted enterprise app catalog. EAM allows for easier discovery, deployment, and updating of prepackaged third-party applications directly from the Intune console, reducing complexity and the time IT admins spend on application packaging and maintenance.
- Microsoft Cloud Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a cloud-based service that simplifies and automates PKI and certificate lifecycle management for Intune-managed devices. It allows organizations to create and manage their cloud-hosted certification authorities (CAs) without needing on-premises servers, connectors, or hardware.
In practice, Intune Suite is for organizations that want a fully managed endpoint environment with no additional purchases. For example, a government agency or large enterprise that needs remote support, strict least-privilege policies, deep analytics, and built-in certificate services would benefit from this license.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, Office 365

Unified Console
Use a single tool to administer and secure AD, Azure AD, and Office 365

Track Threats
Monitor AD for unwanted changes – detect for security or critical functions

Instant Recovery
Recover global enterprise-wide Active Directory forests in minutes, not days
Device-based licensing
Device-based licensing provides an alternative to user-based licensing models that is specifically designed for shared devices and specialty equipment scenarios. This licensing approach enables organizations to manage devices independently of specific user assignments, addressing use cases where traditional user-based licensing models are impractical or cost-prohibitive.
This approach enables device enrollment, configuration policy deployment, and application management without requiring individual user license assignments. Device-based licensing excludes user-centric features like email integration, calendar synchronization, and user-based Conditional Access policies. However, the licenses support device-level compliance policies, application deployment, and security configurations essential for operational functionality.
While device-only licenses offer a potentially more cost-effective way to manage specific endpoints, they have significant functional limitations. It is essential to recognize that these licenses do not support user-based features. Specifically:
- Intune App Protection Policies (APP): Policies that protect organizational data within managed applications cannot be applied based on user identity.
- Conditional Access: Device-based Conditional Access policies, which control access to corporate resources based on device compliance and user context, are not supported.
- User-based management features: Capabilities like email and calendaring configuration tied to a user, or any policy that targets a user identity, will not apply.
- Intune Company Portal: The Company Portal app, typically used by end-users to access corporate apps and manage their enrolled devices, is irrelevant in these “user-less” scenarios.
The primary driver for choosing device-only licenses is often cost reduction, especially when managing a large fleet of devices that fit the “user-less” profile. However, the exclusion of fundamental security features means that organizations must carefully evaluate the security posture of these devices. If they handle sensitive information or access critical network resources, admins should implement alternative or compensating security controls to mitigate potential risks.
License requirement analysis
Choosing the right Intune licenses is not only a procurement task but a strategic decision that directly impacts an organization’s endpoint management capabilities, security posture, and IT budget. Before looking at specific Intune plans, a comprehensive internal assessment is essential to define requirements clearly:
- Count your users and devices: Calculate how many unique users need Intune features and how many devices each will have. Remember that a single user license covers up to 15 devices by default. If you have many shared devices without unique users, calculate whether device licenses or treating them under a user account would be better.
- Basic vs. advanced management needs: If you only need core device management and MAM, Plan 1 suffices (and may already be included in your Microsoft 365/EMS subscriptions). If you need VPN-for-apps (Tunnel) or must manage AR/VR or Teams Rooms, upgrade to Plan 2. If you require certificate management, remote assist, EPM, or analytics, consider the Intune Suite.
- Organization size: Small businesses often use Microsoft 365 Business Premium (which includes Intune Plan 1) and likely need no extra licensing. Mid-sized companies with moderate device variety may stick with Plan 1 and purchase add-ons. Large enterprises (especially global or regulated) often buy Plan 2 add-ons or the full Suite for standardization.
- User types and roles: Frontline workers (deskless/shared scenarios) might be best served with device licenses or Frontline (F3) suites. Knowledge workers on multiple personal devices might be okay with Plan 1 for BYOD. Highly privileged or contractor users might need the least-privileged EPM features of the Suite.
- Cost analysis: Model your costs. For example, 48 shared Macs could be licensed with 48 device licenses ($130/month) or four user licenses covering 60 devices ($32/month). Factor in the number of admin accounts and device usage when deciding between device and user licensing.
In summary, start with a basic inventory: How many users, how many endpoints, and what special cases? Then map to Intune features: If 90% of needs are satisfied by core features, Plan 1 is adequate. Finally, identify scenarios that require a higher tier (Tunnel VPN, specialized hardware, advanced analytics, etc.).
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams
| Platform | Admin Features | Single Console for Hybrid (On-prem AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams) | Change Monitoring & Auditing | User Governance (Roles, Rules, Automation) | Forest Recovery in Minutes |
| Microsoft AD Native Tools | ✓ | ||||
| Microsoft AD + Cayosoft | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
License management and cost optimization
Acquiring the correct Microsoft Intune licenses is only the first step. IT admins need to effectively manage and optimize the licenses to ensure cost-effectiveness, maintain compliance, and maximize the value of the investment.
Use the Microsoft 365 admin center or Azure AD reports to track license assignments. You can filter active users by assigned Intune or Microsoft 365 licenses and export the list. Alternatively, use third-party solutions like Cayosoft to gain visibility and control your Microsoft Office 365 licenses. Identify unused or redundant licenses (e.g., old user accounts, duplicates) and reassign or remove them.
Implement Conditional Access policies that require devices to be Intune-enrolled and compliant to access corporate resources. This indirectly enforces licensing compliance—users without proper Intune licenses cannot get device compliance status and thus are blocked.
Control who can assign licenses using Azure AD Privileged Identity Management or custom RBAC. For instance, only allow certain IT admin roles to manage Intune licenses, so you don’t accidentally over-assign.
Reporting tools and careful governance ensure that each user or device has the minimum license necessary. For example, avoid giving a full Suite license to every user if only a handful of power users need its features. Likewise, ensure that shared devices
Conclusion
Success requires moving beyond feature comparisons to understanding how each licensing tier aligns with your risk tolerance, compliance requirements, and growth trajectory. For organizations seeking to maximize their Intune investment while ensuring comprehensive endpoint protection, partnering with specialists who understand both Microsoft’s licensing complexities and real-world implementation challenges is invaluable.
Schedule a demo to learn how Cayosoft’s expertise in Microsoft ecosystem management can help translate licensing options into actionable security strategies tailored to your specific operational requirements.
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content