Microsoft Entra app with client secrets
Cayosoft Threat Definition CTD-000008
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Risk Summary
Client secrets in Microsoft Entra app registrations are easily leaked (config files, scripts, CI/CD logs). If compromised, attackers can use the app’s granted permissions to operate as the application and access data or perform actions.
- Severity: Medium
- Platform: Entra ID
- Category: Infrastructure
- MITRE ATT&CK Tactics: Defense Evasion, Credential Access
- MITRE D3FEND Tactics: Application Configuration Hardening
Description
App registration with client secrets poses a threat. A client secret is a string value that might be used in config files or scripts, and it can be easily compromised. Once the secret is compromised, any permissions granted to the service principal can be used by a threat actor to perform actions on behalf of an application.

Real-World Scenario
An engineer creates an app registration for a build pipeline and adds a long-lived client secret. The secret is copied into a YAML file and later appears in pipeline logs. An external attacker who accesses those logs replays the secret to obtain OAuth tokens and calls Microsoft Graph with the app’s Application permissions to read mailboxes and modify Entra settings. Because the actions run “as the app,” traditional user-based alerts are bypassed. Cayosoft Guardian flags CTD-000008 when it detects app registrations that still rely on client secrets, enabling response before the secret is abused.
Stop Privilege Escalation—Then Undo It with Cayosoft Guardian
Real-time alerts across AD & Entra ID with one-click rollback.
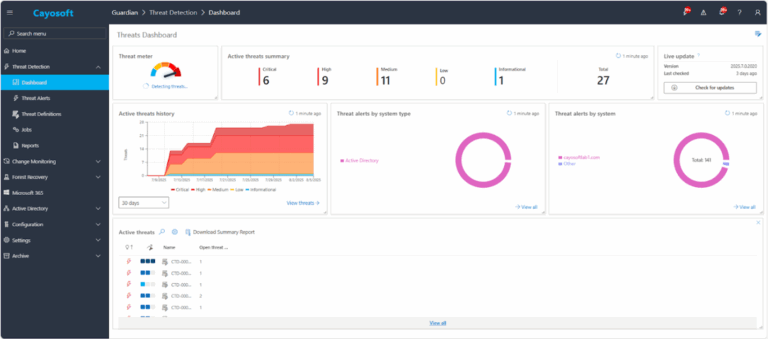
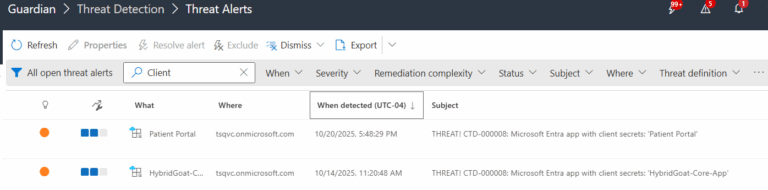
2.) View All Alerts and search for CTD-000008 or Microsoft Entra app with client secrets.
3.) Open any alert and Click for details (from Raise Threat Alert action).
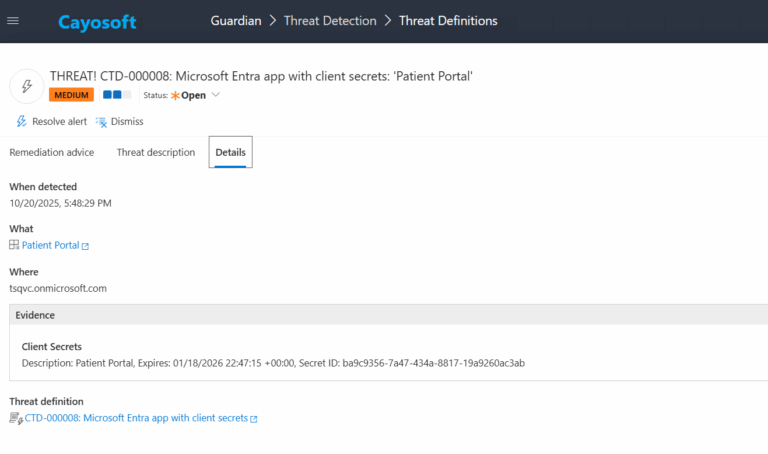
Evidence
- Client Secrets
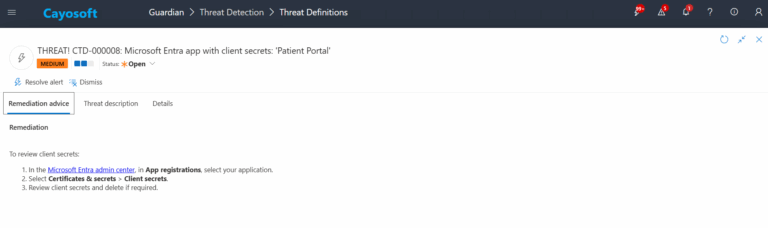
Remediation Steps
- ) In the Microsoft Entra admin center, in App registrations, select your application.
- ) Select Certificates & secrets > Client secrets.
- ) Review client secrets and delete if required.
How to Prevent It
- Use certificates or managed identity instead of client secrets wherever possible.
- If secrets are unavoidable, enforce short lifetimes and automatic rotation.
- Grant least privilege to the app’s service principal; avoid broad Application permissions.
- Store secrets only in secure stores (e.g., Key Vault) and prevent logging of secrets in CI/CD.
- Continuously monitor with Cayosoft Guardian, which detects and alerts on Microsoft Entra app with client secrets across Entra ID, Microsoft 365, and Intune.
FAQ
Client secrets are static strings that can be accidentally exposed in scripts, config files, or CI/CD logs. If an attacker obtains the secret, they can authenticate as the application and use its permissions to access data or modify settings. Since the actions run “as the app,” they often bypass traditional user-based monitoring and alerts, making detection harder.
Tools like Cayosoft Guardian can detect and alert when app registrations rely on client secrets. In the Microsoft Entra admin center, you can review app registrations under Certificates & secrets → Client secrets to identify applications still using them. Regular monitoring ensures early detection before secrets are leaked or abused.
Replace client secrets with more secure alternatives like certificates, federated credentials, or managed identities. If a secret must remain, enforce short expiration, document a strict rotation policy, and store secrets only in secure vaults. Also, grant the service principal only the minimum necessary permissions to reduce the blast radius if a secret is compromised.
Final Thought
Proactive monitoring and timely remediation of configuration risks is essential to maintaining a secure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 environment. By addressing issues like Microsoft Entra app with client secrets, you reduce attack surfaces and strengthen your organization’s overall security posture.