Home » Your Guide to Secure Endpoint Management: Essential Microsoft Intune Features » A Guide to Microsoft Intune Management Extension Deployment
A Guide to Microsoft Intune Management Extension Deployment
Learn how to use Microsoft Intune Management Extension for granular device control and complex application management on Windows devices in this step-by-step guide.
Explore the chapters:
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Microsoft Intune provides a comprehensive solution for Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Mobile Application Management (MAM). However, in complex environments and organizational structures, IT administrators often need more device customizations, such as running custom scripts or deploying complex Win32 applications. Microsoft Intune Management Extension is a versatile add-on that enables granular device control, which is necessary for complex operating environments.
This article will explore Microsoft Intune Management Extension, its integration with Windows device management through Intune, and explain how to use Microsoft Intune Management Extension step-by-step.
Summary of key Intune Management Extension concepts
The following table lists nine important aspects of the Microsoft Intune Management Extension.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Supported operating system (OS) | Windows 10 (1607 or later) and 11 only |
| Installation method | Automatic |
| Default sync period | Every 8 hours |
| Manual Sync supported | Yes |
| Installation folder | C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Intune Management Extension\ |
| Log location | C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs |
| Important logs | IntuneManagementExtension.log, AgentExecutor.log, AppWorkload.log, Win32AppInventory.log |
| PowerShell script retry | Three times, once every 60 minutes or when the device reboots |
| Win32 app retry | Three times, once every 5 minutes, and then after 24 hours. |
Learn About The First-Ever Monitoring and Rollback for Microsoft Intune
Overview of Microsoft Intune Management Extension
Microsoft Intune Management Extension enables complex device and application management capabilities on Windows devices by extending Intune’s native Windows device management (Mobile Device Management or MDM) functionality.
The extension enables organizations and administrators to meet features such as executing custom PowerShell scripts, deploying and managing Win32 applications not supported by standard Intune app types, enforcing granular configuration policies beyond the standard MDM policies, and monitoring compliance status on devices using custom settings.
Supported operating systems
The Microsoft Intune Management Extension is currently supported only on Windows 10 (1607 or later) and Windows 11 devices as of this writing.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites for using the Microsoft Intune Management Extension are:
- .NET Framework 4.7.2 or higher.
- Windows 10 version 1607 or later.
- Windows 10 version 1709 or later when devices are enrolled using bulk auto-enrollment.
- For PowerShell scripts, PowerShell 5.1 or newer is required.
- Devices must be joined through Entra ID join or Hybrid Entra ID join, and also enrolled in Intune.
- Note: Microsoft Entra registered and workplace-joined devices are also supported.
- Devices must be able to access Intune endpoints. Check out the official Microsoft documentation for the complete list of supported devices.
Supported capabilities
IT administrators can perform the following advanced tasks using Intune Management Extension:
- PowerShell script execution: Using the Intune Management Extension, administrators can remotely run PowerShell scripts addressing various scenarios on supported and enrolled Windows devices. These scenarios include configuration tasks, applying security policies, proactive remediation of known issues, or troubleshooting.
- Win32 application deployment: Organizations with legacy or custom Win32 applications can use the Intune Management Extension to manage applications that Intune cannot otherwise manage.
- Custom compliance and policy enforcement: Organizations can run custom scripts to monitor compliance, thus enabling policy enforcement to maintain compliance. For example, a discovery script can check for device settings and report their status.
How Microsoft Intune Management Extension works
The installation of the Microsoft Intune Management Extension is automatically triggered on Windows 10 and 11 devices that meet the above prerequisites. Additionally, at any time, PowerShell, Win32 apps, or other advanced management features can be assigned to them. The following are other features that, when assigned, trigger an installation:
- Remediation scripts
- Discovery scripts for custom compliance
- Endpoint analytics
- Remote help
- Managed Installers in Intune
- Update Windows BIOS by configuring the MDM policy
- Microsoft Store apps
The installation process is silent. Once an Intune Management Extension is installed on a device, it signs in with Intune services for authentication and receives its assigned features.
If a PowerShell script installation fails, it is retried up to three times, once every 60 minutes, or when the device reboots. Similarly, if a Win32 app installation fails, the Intune Management Extension will retry three times with a 5-minute gap and then retry after 24 hours.
Watch a 15-minute Demo of Microsoft Intune Change Monitoring and Recovery
Microsoft Intune Management Extension sync frequency
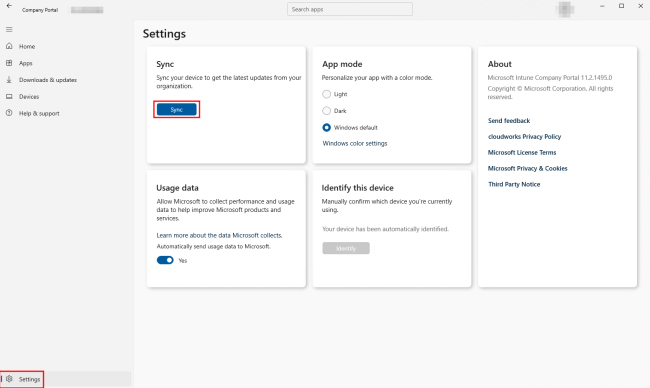
By default, Intune Management Extension syncs every 8 hours. You can also manually sync a managed device from either the Company Portal app or using the Task Manager.
For example, on a Windows device, launch the Company Portal app. Select Settings in the bottom left corner, and then click the Sync button.
How to verify a Microsoft Intune Management Extension installation
There are several ways to verify an Intune Management Extension installation. Here are five of them:
- The C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Intune Management Extension\ folder, where the extension is installed.
- The Microsoft Intune Management Extension service in Windows Services.
- The registry entries at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension.
- The scheduled tasks in Windows Task Scheduler for Sync and Client Health.
- The log files in C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs\.
Later, in the ‘How to use Microsoft Intune Management Extension’ section, we will see how to verify an installation using some of these methods.
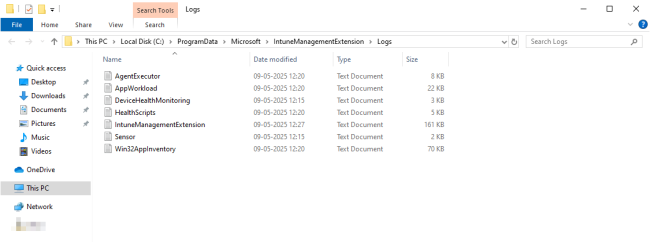
Microsoft Intune Management Extension logs and their location
As mentioned earlier, the logs for Intune Management Extension are located at C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs\.
The following table lists the logs and their contents. Note that you may not see all of these log files in every installation.
| Log File | Description |
|---|---|
| AgentExecutor | This log file contains information on all the PowerShell scripts that are executed. |
| AppActionProcessor | It contains information about Win32 app deployments related to the execution and state transition of actions. |
| AppWorkload | It contains information on Win32 application deployment activities. |
| ClientCertCheck | This log file contains the status of client certificates, such as whether they are present, when they expire, and errors. |
| ClientHealth | The log file contains information on the health status of the device’s Intune Management Extension. |
| DeviceHealthMonitoring | This log file contains records on the collection and reporting of device health metrics used by Endpoint Analytics. |
| HealthScripts | It contains information on the health scripts that run on schedule by the Intune Management Extension. |
| IntuneManagementExtension | It is the primary log file that records all Intune Management Extension activities. |
| Sensor | This file contains health information of the Endpoint analytics data collector, including boot performance, app reliability, and more. |
| Win32AppInventory | This log file contains information about the discovery and inventory of Win32 applications. |
Removal scenarios for Microsoft Intune Management Extension
In the event that any of these conditions are met, the Microsoft Intune Management Extension may be removed:
- When there are no scripts or apps assigned to the device.
- When Intune MDM no longer manages the device.
- Errors leading to an irrecoverable state for over 24 hours.
Learn the best practices for Intune monitoring, security, and recovery
How to use Microsoft Intune Management Extension
Let’s learn how to use Microsoft Intune Management Extension to deploy a PowerShell script on a Windows device. The device used in this demonstration meets the prerequisites: it is Microsoft Entra-joined and Microsoft Intune-managed.
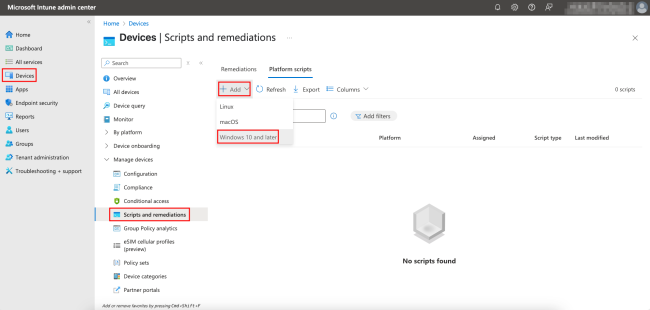
First, go to the Microsoft Intune admin center at https://intune.microsoft.com/ and log in.
Navigate to Devices, select the Scripts and remediations option under Manage devices, and then choose the Platform scripts tab. Click + Add and select Windows 10 and later.
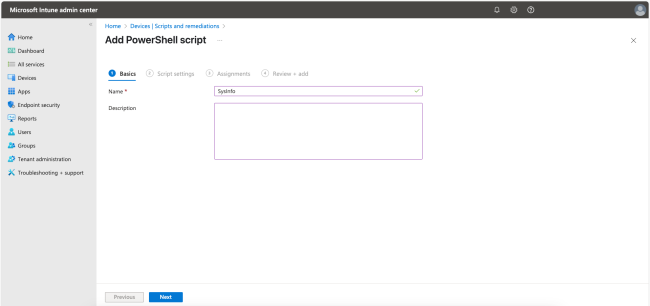
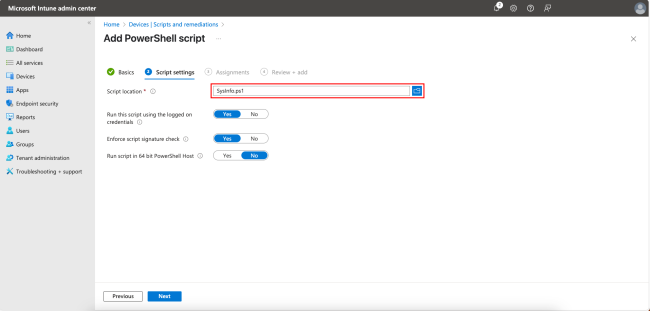
In the following steps, we will add a PowerShell script. Start by giving the script a Name. Click Next to continue.
In the next step, browse and select the PowerShell script location. You can also choose whether to run the script using logged-on credentials or in the system context, whether to enforce script signature checks, and whether to run the script in 64-bit or 32-bit mode. In this example, we’ll use the defaults. Click Next.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, Office 365

Unified Console
Use a single tool to administer and secure AD, Azure AD, and Office 365

Track Threats
Monitor AD for unwanted changes – detect for security or critical functions

Instant Recovery
Recover global enterprise-wide Active Directory forests in minutes, not days
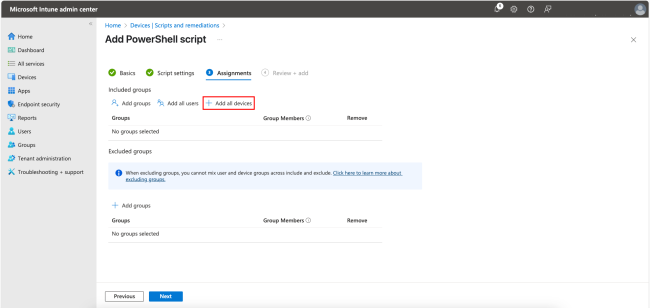
In this step, you will assign groups, users, and devices to the script. You can also exclude certain groups. For this example, click + Add all devices to include only devices for pushing and click Next.
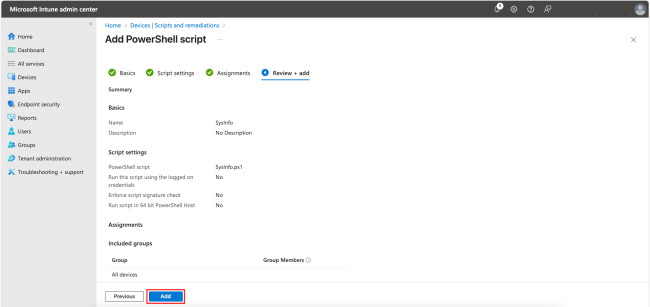
In the final step, review the settings and click Add to complete the process.
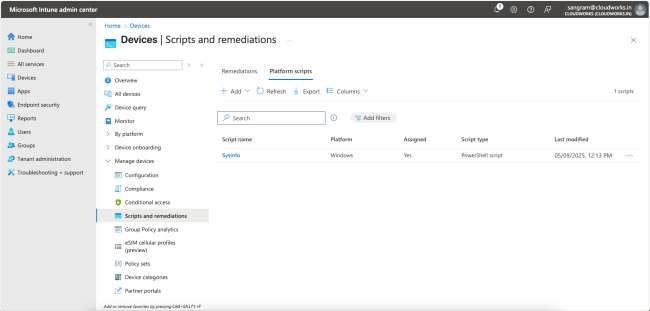
You should now see the script on the list. Monitor until the Assigned status changes to Yes.
Verify Intune Management Extension installation
In this section, we will learn how to verify that the Microsoft Intune Management Extension was pushed to the device by checking the program files and logs folders.
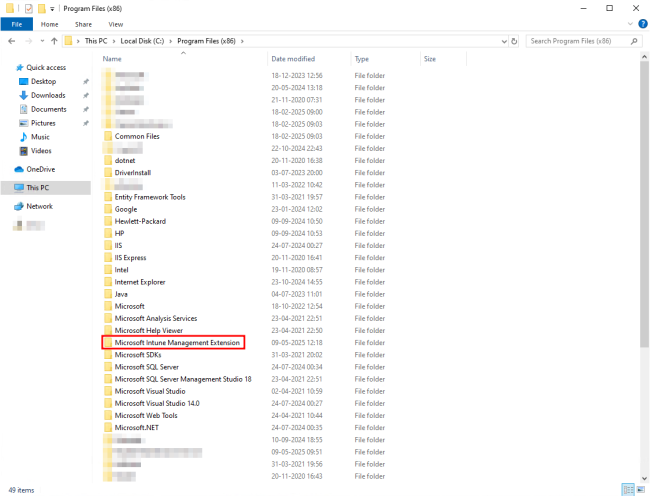
- Navigate to C:\Program Files (x86)\ in Windows Explorer and check for the Microsoft Intune Management Extension folder as shown in the figure below.
Similarly, navigate to the C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs\ folder to see the log files as demonstrated in the image below.
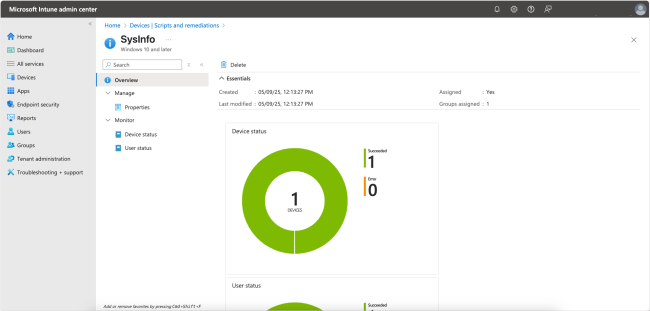
Monitoring device status
You have a couple of places where you can monitor the script’s status. In the Overview page, you can view the overall status.
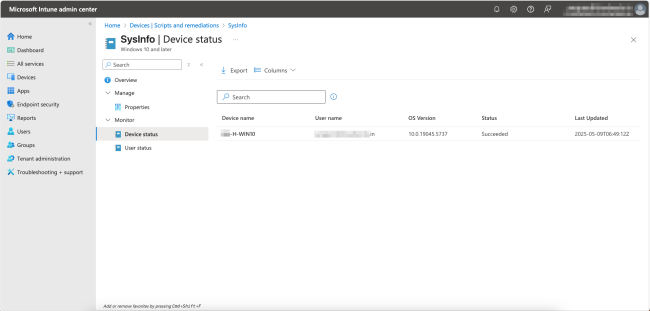
The monitor section on the page allows you to view the individual status of devices or users. For our example, click on Device status under Monitor to see a table view of the device name, the user name, the OS version, the current status, and when it was last updated. Please note that it may take some time for the device status to be reflected here.
Manage, Monitor & Recover AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams
| Platform | Admin Features | Single Console for Hybrid (On-prem AD, Azure AD, M365, Teams) | Change Monitoring & Auditing | User Governance (Roles, Rules, Automation) | Forest Recovery in Minutes |
| Microsoft AD Native Tools | ✓ | ||||
| Microsoft AD + Cayosoft | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Conclusion
Microsoft Intune Management Extension is a sidecar agent supporting advanced configuration use cases, custom scripts, and application deployments. It significantly expands Intune’s MDM capabilities for Windows 10/11 devices, providing the flexibility that enterprises need.
It enables IT administrators to address scenarios such as running proactive remediation scripts, meeting custom compliance requirements, or endpoint management at a granular level, which is what standard Intune provides. The Intune Management Extension operates silently as a background service, requiring no user involvement or interruptions, making it a valuable addition to modern endpoint management for Windows devices.
However, the complexity of managing Intune deployments at scale introduces significant challenges. Cayosoft Guardian provides real-time hybrid identity protection that extends to comprehensive Intune monitoring and management.
As part of Cayosoft’s suite of products designed specifically for Microsoft environments, Guardian monitors changes within Intune alongside Active Directory, Entra ID, and Teams, offering:
- Real-time change monitoring and alerting for Intune configurations
- Complete audit trails for compliance and forensic analysis
- Instant rollback capabilities for unauthorized or problematic changes
- Automated object protection to prevent critical configuration modifications
Ready to see how continuous monitoring and instant rollback can transform your Intune management strategy? Schedule a demo of Cayosoft Guardian to discover how real-time protection and recovery capabilities can secure your Microsoft ecosystem while reducing administrative overhead.
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content