Resource-based constrained delegation on domain controllers
Cayosoft Threat Definition CTD-000138
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Risk Summary
Modifying the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity attribute can have serious security implications, especially when applied to domain controllers that handle highly privileged operations.
- Severity: High
- Platform: Active Directory
- Category: Kerberos
- MITRE ATT&CK Tactics: Defense Evasion, Lateral Movement, Privilege Escalation
MITRE D3FEND Tactics: Credential Hardening
Description
Modifying the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity attribute can have security implications, so administrators should avoid assigning delegation to privileged resources such as domain controllers. Resource-based constrained delegation (RBCD) is configured on the target resource, unlike other delegation types that are configured on the accounts accessing the resource.
When a threat actor gains control over a service account, improperly configured RBCD settings can be exploited. These misconfigurations can allow the attacker to delegate credentials from a lower-privileged account to a higher-privileged resource and thereby escalate privileges.
Configuring RBCD on domain controllers allows specific accounts to impersonate other users when accessing particular resources. This provides granular control over delegation permissions focused on the resource rather than the service account. However, when RBCD is misconfigured on domain controllers, it becomes a significant security risk and a powerful lateral movement and privilege escalation vector.

Real-World Scenario
An attacker first compromises a low-privileged service account through stolen credentials. After gaining a foothold, the attacker discovers that resource-based constrained delegation is configured on a domain controller and that the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity attribute includes the compromised service account. By abusing this configuration, the attacker forges Kerberos tickets that impersonate highly privileged users when connecting to services on the domain controller. The attacker then escalates privileges to domain admin and deploys additional persistence mechanisms while avoiding obvious logon anomalies. Cayosoft Guardian would detect the risky RBCD configuration on domain controllers and raise a threat alert before the attacker could fully exploit the misconfiguration.
Stop Privilege Escalation—Then Undo It with Cayosoft Guardian Audit & Restore
Real-time alerts across AD & Entra ID with one-click rollback.
Detect this and other threats with Cayosoft Guardian Protector (Free of Charge)
1.) Download Cayosoft Guardian Protector for free real-time threat detection and monitoring of your hybrid AD and Microsoft 365 environment. Once downloaded, sign in and navigate to the Threat Detection Dashboard.
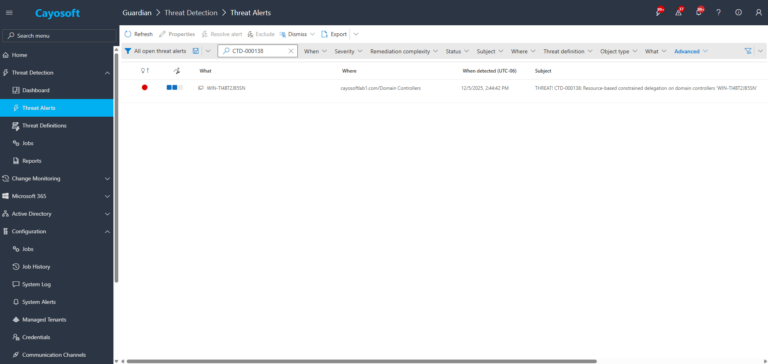
2.) Go to All Alerts and search for CTD-000138 or “Resource-based constrained delegation on domain controllers”.
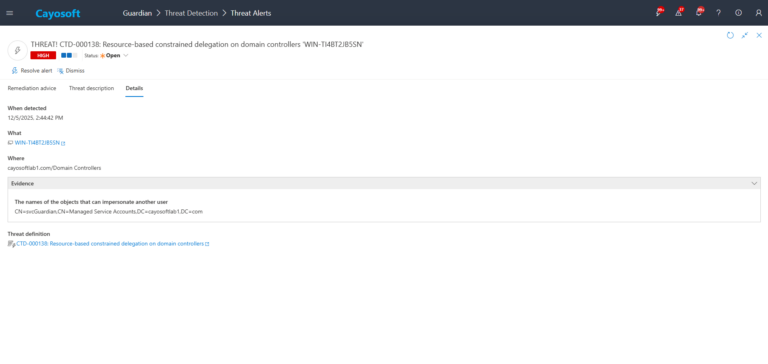
3.) Open any alert and Click for details (from Raise Threat Alert action).
4.) Evidence:
- The names of the objects that can impersonate another user
Remediation Steps
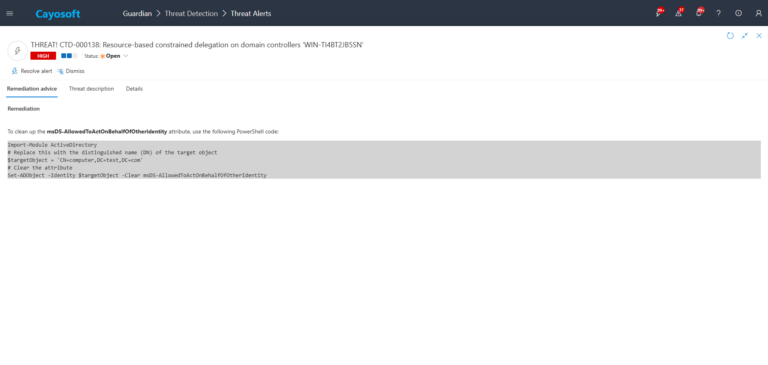
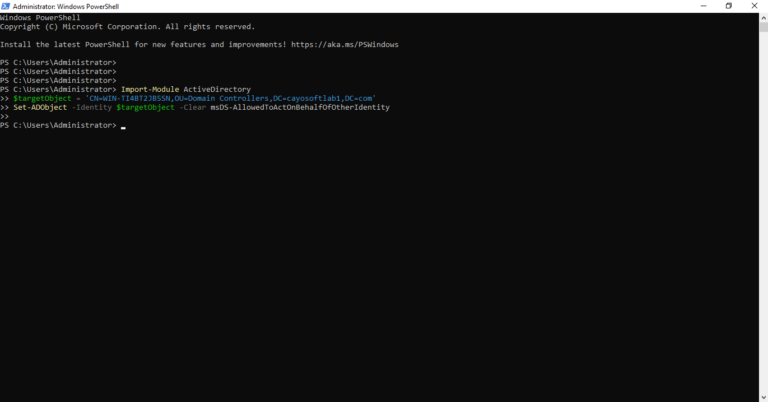
To clean up the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity attribute, use the following PowerShell code:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
# Replace this with the distinguished name (DN) of the target object
$targetObject = 'CN=computer,DC=test,DC=com'
# Clear the attribute
Set-ADObject -Identity $targetObject -Clear msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentityHow to Prevent It
- Avoid configuring resource-based constrained delegation on domain controllers unless there is a clearly documented and justified requirement.
- Regularly review the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity attribute on domain controllers and other high-value assets to ensure only authorized principals are present.
- Limit which service accounts can use RBCD and ensure those accounts are tightly controlled, monitored, and protected with strong credential hygiene.
- Use Cayosoft Guardian to continuously monitor for new or changed RBCD configurations that involve domain controllers or other privileged resources.
Cayosoft Guardian can proactively detect and alert on Resource-based constrained delegation on domain controllers. It continuously monitors Active Directory, Entra ID, Microsoft 365, and Intune for over 200 misconfigurations, providing early warning before attackers can exploit them.
FAQ
Because RBCD allows designated accounts to impersonate other users, applying it to domain controllers enables impersonation of highly privileged identities. A misconfiguration, especially combined with a compromised service account, can result in full domain compromise.
This attribute defines which security principals may impersonate other users for a specific resource. When set on a domain controller, it determines who can leverage RBCD against that domain controller.
Yes. If a low-privileged or compromised service account is included in the RBCD configuration of a domain controller, an attacker can impersonate privileged users, forge Kerberos tickets, and escalate to domain admin.
Yes. Native AD tools and PowerShell can locate msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity entries, and Cayosoft Guardian Protector provides free detection of dangerous RBCD configurations without requiring a full license.
Yes. Cayosoft Guardian continuously monitors AD for misconfigured RBCD, raises CTD-000138 alerts, and provides prescriptive remediation guidance to help administrators remove unauthorized delegation safely.
Final Thought
Proactive monitoring and timely remediation of configuration risks is essential to maintaining a secure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 environment. By addressing issues like Resource-based constrained delegation on domain controllers, you reduce attack surfaces and strengthen your organization’s overall security posture.