Active Directory dangerous user rights assignments on domain controllers
Cayosoft Threat Definition CTD-000172
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Risk Summary
Dangerous User Rights Assignment on domain controllers grants powerful local privileges (for example, Act as part of the operating system, Debug programs, Impersonate a client after authentication). If assigned to non-administrative principals, attackers can escalate privileges, maintain persistence, or bypass protections.
- Severity: High
- Platform: Active Directory
- Category: Infrastructure, Privileged Access Management
- MITRE ATT&CK Tactics: Persistence, Privilege Escalation, Defense Evasion
- MITRE D3FEND Tactics: D3-APA (Access Policy Administration)
Description
Windows user rights govern sensitive local privileges on domain controllers. Granting rights like SeTcbPrivilege (Act as part of the operating system), SeDebugPrivilege (Debug programs), or SeImpersonatePrivilege to non-standard accounts enables code injection, token manipulation, and stealthy lateral movement. Domain controllers should restrict these rights to trusted security principals only (typically BUILTIN\Administrators, LOCAL SYSTEM, and vetted service accounts with documented justification).

Real-World Scenario
A legacy monitoring agent runs under a generic domain user that was mistakenly granted Debug programs and Impersonate a client after authentication on all DCs. A threat actor who compromises that account injects into LSASS to extract credentials, then uses impersonation to run scheduled tasks as SYSTEM. Because these are configured “rights,” the behavior blends with normal OS functions and evades many detections. Within hours the attacker establishes a hidden admin and disables auditing. Cayosoft Guardian would flag the dangerous user rights on DCs so admins can remove the assignments before they are abused.
Stop Privilege Escalation—Then Undo It with Cayosoft Guardian Audit & Restore
Real-time alerts across AD & Entra ID with one-click rollback.
Detect this and other threats with Cayosoft Guardian Protector (Free of Charge)
1.) Download Cayosoft Guardian Protector for free real-time threat detection and monitoring of your hybrid AD and Microsoft 365 environment. Once downloaded, sign in and navigate to the Threat Detection Dashboard.
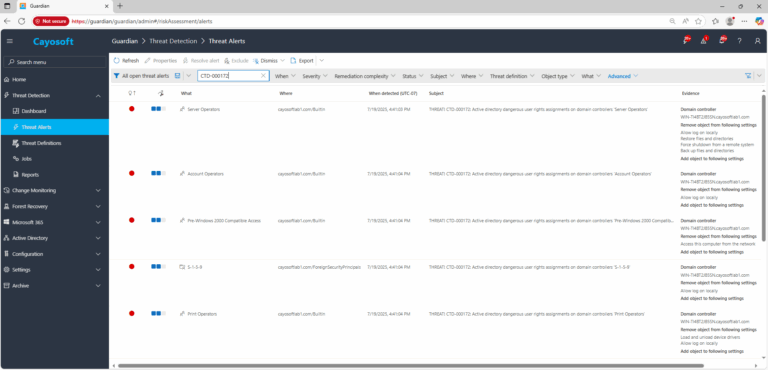
2.) Open All Alerts and search for CTD-000172 or “Active Directory dangerous user rights assignments on domain controllers.”
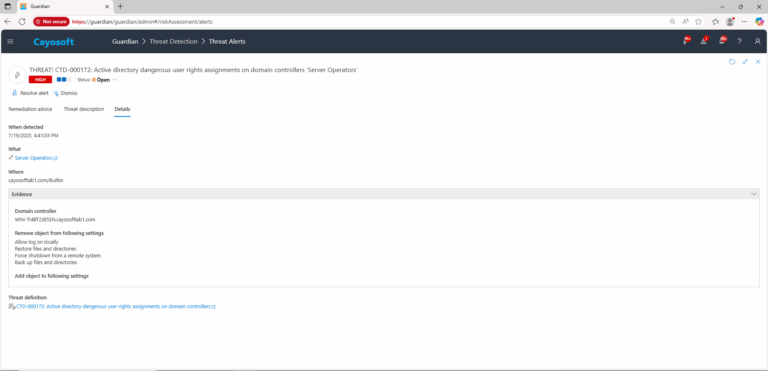
3.) Open any alert and Click for details (from Raise Threat Alert action).
4.) Evidence (fields)
- Domain controller
- Remove object from following settings
- Add object to following settings
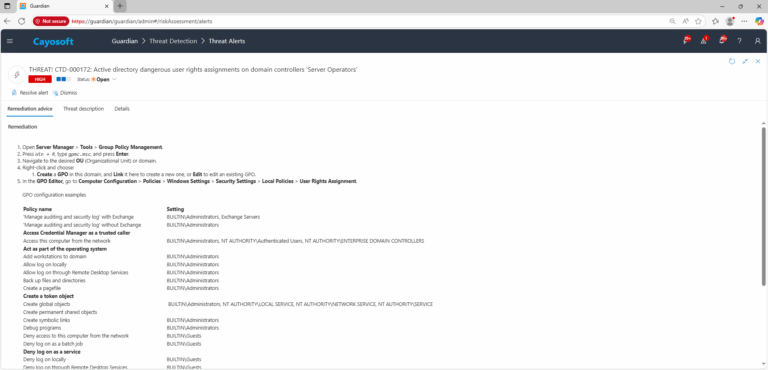
Remediation Steps
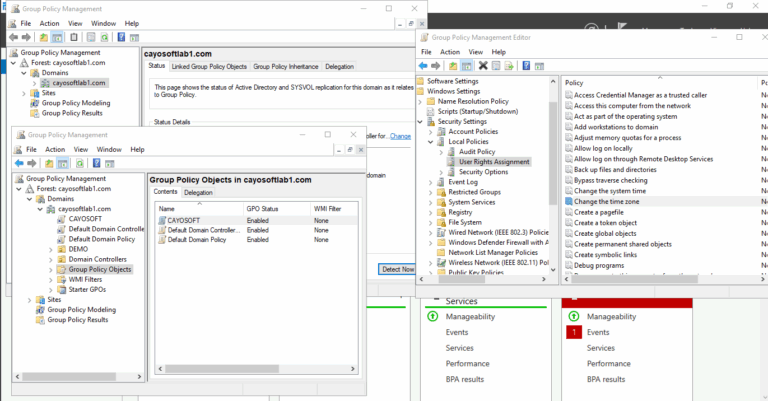
- ) Open Server Manager > Tools > Group Policy Management.
- ) Press
Win + R, typegpmc.msc, and press Enter. - ) Navigate to the desired OU (Organizational Unit) or domain.
- ) Right-click and choose:
- Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here to create a new one, or Edit to edit an existing GPO.
- ) In the GPO Editor, go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment.
GPO configuration examplesPolicy name Setting ‘Manage auditing and security log’ with Exchange BUILTIN\Administrators, Exchange Servers ‘Manage auditing and security log’ without Exchange BUILTIN\Administrators Access Credential Manager as a trusted caller Access this computer from the network BUILTIN\Administrators, NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users, NT AUTHORITY\ENTERPRISE DOMAIN CONTROLLERS Act as part of the operating system Add workstations to domain BUILTIN\Administrators Allow log on locally BUILTIN\Administrators Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services BUILTIN\Administrators Back up files and directories BUILTIN\Administrators Create a pagefile BUILTIN\Administrators Create a token object Create global objects BUILTIN\Administrators, NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE Create permanent shared objects Create symbolic links BUILTIN\Administrators Debug programs BUILTIN\Administrators Deny access to this computer from the network BUILTIN\Guests Deny log on as a batch job BUILTIN\Guests Deny log on as a service Deny log on locally BUILTIN\Guests Deny log on through Remote Desktop Services BUILTIN\Guests Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation BUILTIN\Administrators Force shutdown from a remote system BUILTIN\Administrators Generate security audits NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE Impersonate a client after authentication NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE, NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE, BUILTIN\Administrators Increase scheduling priority BUILTIN\Administrators Load and unload device drivers BUILTIN\Administrators Lock pages in memory Modify firmware environment values BUILTIN\Administrators Perform volume maintenance tasks BUILTIN\Administrators Profile single process BUILTIN\Administrators Restore files and directories BUILTIN\Administrators Take ownership of files or other objects BUILTIN\Administrators
How to Prevent It
Cayosoft Guardian can proactively detect and alert on Active Directory dangerous user rights assignments on domain controllers. It continuously monitors Active Directory, Entra ID, Microsoft 365, and Intune for over 200 misconfigurations, providing early warning before attackers can exploit them.
FAQ
User rights like Act as part of the operating system, Debug programs, or Impersonate a client after authentication grant powerful local privileges. If assigned to non-admins, attackers can escalate privileges, steal credentials, or bypass defenses.
Only when technically required and fully documented. Default configuration should limit these rights to Administrators, Local System, or vetted service accounts with a clear business justification.
Review applied Group Policy settings under Local Policies → User Rights Assignment on a domain controller. Confirm that only approved groups (typically Administrators or required service accounts) hold sensitive privileges.
Final Thought
Proactive monitoring and timely remediation of configuration risks is essential to maintaining a secure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 environment. By addressing issues like Active Directory dangerous user rights assignments on domain controllers, you reduce attack surfaces and strengthen your organization’s overall security posture.