The certificate template has a key length of less than 2048 bits
Cayosoft Threat Definition CTD-000158
Stop AD Threats As They Happen
Cayosoft Protector provides continuous monitoring and real-time alerts across your entire Microsoft Identity stack
Like This Article?
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to receive more educational content
Risk Summary
A threat actor can exploit weak or vulnerable certificates by abusing inherent weaknesses such as poor random number generation, small key size, and susceptibility to side-channel attacks. Certificates issued from a template with a key length of less than 2048 bits are significantly easier to break or forge, enabling impersonation and unauthorized access. Replacing vulnerable keys with stronger algorithms and key sizes reduces this risk and aligns with modern cryptographic standards.
- Severity: High
- Platform: Active Directory
- Category: Certificate Services (ADCS), Infrastructure
- MITRE ATT&CK Tactics: Privilege Escalation
- MITRE D3FEND Tactics: Credential Hardening
Description
A threat actor can exploit weak or vulnerable certificates by abusing several inherent weaknesses, particularly random number generation, key size, and susceptibility to side-channel attacks. Replacing vulnerable keys with more modern and secure cryptographic algorithms mitigates these risks. To secure the environment, it is essential to phase out weak certificates, revoke any currently issued weak certificates, and replace them with certificates using stronger algorithms and key sizes.

Real-World Scenario
An attacker gains a low-privileged account in the domain and discovers an ADCS certificate template that issues certificates with a 1024-bit RSA key. The attacker enrolls a certificate from this template for a service or user that has elevated access and captures the issued certificate for offline analysis. Using cloud resources or specialized hardware, the attacker focuses on the weaker 1024-bit key to derive or otherwise compromise the private key, then uses the resulting certificate to impersonate the privileged user or system. Because the attacker uses standard certificate enrollment flows and valid ADCS infrastructure, the activity appears similar to normal PKI operations and avoids obvious detection. Cayosoft Guardian’s CTD-000158 threat definition detects certificate templates with key lengths below 2048 bits so administrators can remediate the weakness before an attacker can exploit it.
Stop Privilege Escalation—Then Undo It with Cayosoft Guardian Audit & Restore
Real-time alerts across AD & Entra ID with one-click rollback.
Detect this and other threats with Cayosoft Guardian Protector (Free of Charge)
1.) Download Cayosoft Guardian Protector for free real-time threat detection and monitoring of your hybrid AD and Microsoft 365 environment. Once downloaded, sign in and navigate to the Threat Detection Dashboard.
2.) Open All Alerts and search for CTD-000158 or “The certificate template has a key length of less than 2048 bits.”
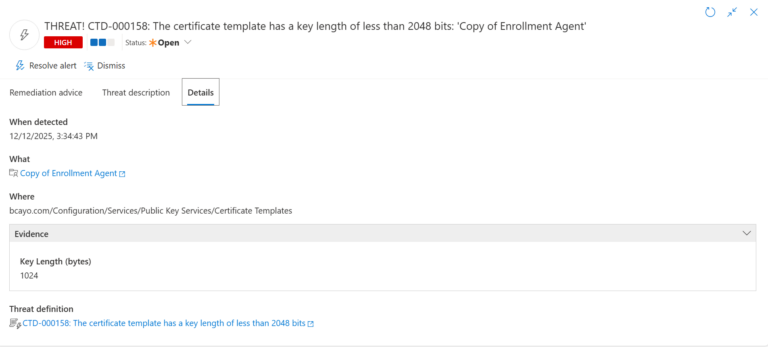
3.) Open any alert and Click for details (from Raise Threat Alert action).
4.) Evidence:
- Key Length (bytes) – {TargetItem/msPKI_Minimal_Key_Size}
Remediation Steps
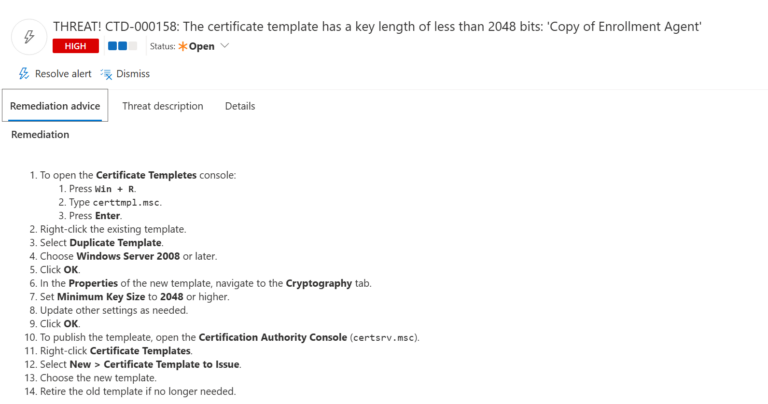
- ) To open the Certificate Templetes console:
- ) Press
Win + R. - ) Type
certtmpl.msc. - ) Press Enter.
- ) Press
- ) Right-click the existing template.
- ) Select Duplicate Template.
- ) Choose Windows Server 2008 or later.
- ) Click OK.
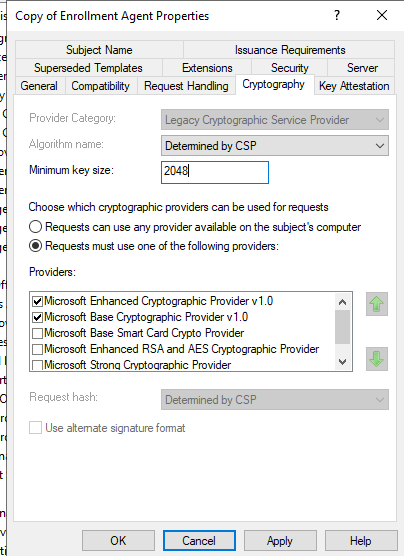
- ) In the Properties of the new template, navigate to the Cryptography tab.
- ) Set Minimum Key Size to 2048 or higher.
- ) Update other settings as needed.
- ) Click OK.
- ) To publish the templeate, open the Certification Authority Console (
certsrv.msc). - ) Right-click Certificate Templates.
- ) Select New > Certificate Template to Issue.
- ) Choose the new template.
- ) Retire the old template if no longer needed.
How to Prevent It
- Standardize on 2048-bit or higher key lengths for all ADCS certificate templates, or stronger according to current cryptographic guidance.
- Periodically review ADCS templates to ensure no new templates are created with key sizes below the approved baseline.
- Use Cayosoft Guardian to continuously monitor ADCS templates and trigger CTD-000158 alerts whenever a certificate template has a key length of less than 2048 bits.
- Implement a formal PKI governance process so new templates and changes to existing templates are reviewed and approved by security and PKI owners.
- Revoke or phase out certificates that were issued using weak templates and reissue them using hardened templates.
FAQ
Keys shorter than 2048 bits use weaker cryptography that is significantly easier to break or abuse, increasing the risk of certificate forgery, impersonation, and unauthorized access.
An attacker could enroll a certificate from the weak template, compromise or forge the key, and then use the certificate to authenticate as a user, service, or computer with elevated privileges.
Cayosoft Guardian continuously analyzes ADCS certificate template settings and flags templates that do not meet modern cryptographic baselines, including minimum key length requirements.
Cayosoft Guardian provides early detection, detailed evidence, and guided remediation so administrators can harden certificate templates before attackers exploit weak cryptography.
Final Thought
Proactive monitoring and timely remediation of configuration risks is essential to maintaining a secure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 environment. By addressing issues like The certificate template has a key length of less than 2048 bits, you reduce attack surfaces and strengthen your organization’s overall security posture.